Tuesday, 30 June 2020
International Asteroid Day 🌑🎉🎊🎂🎈🌠
The United Nations declared 30 June as International Asteroid Day to educate the public about asteroids. The date of International Asteroid Day commemorates the anniversary of the Tunguska asteroid impact over Siberia, Russian Federation, on 30 June 1908.

⚛Asteroids are minor planets, especially of the inner Solar System.
The Asteroids vary greatly in size, from almost 1000 km for the largest down to rocks just 1 meter acrosse, much smaller than planets in Asteroid belt lies between Mars and Jupiter. Larger asteroids have also been called planetoids.
They are not visible from Earth🌎 with the naked eye, but many may be seen through binoculars or small
telescopes🔭.
Asteroids made of:🤔❔
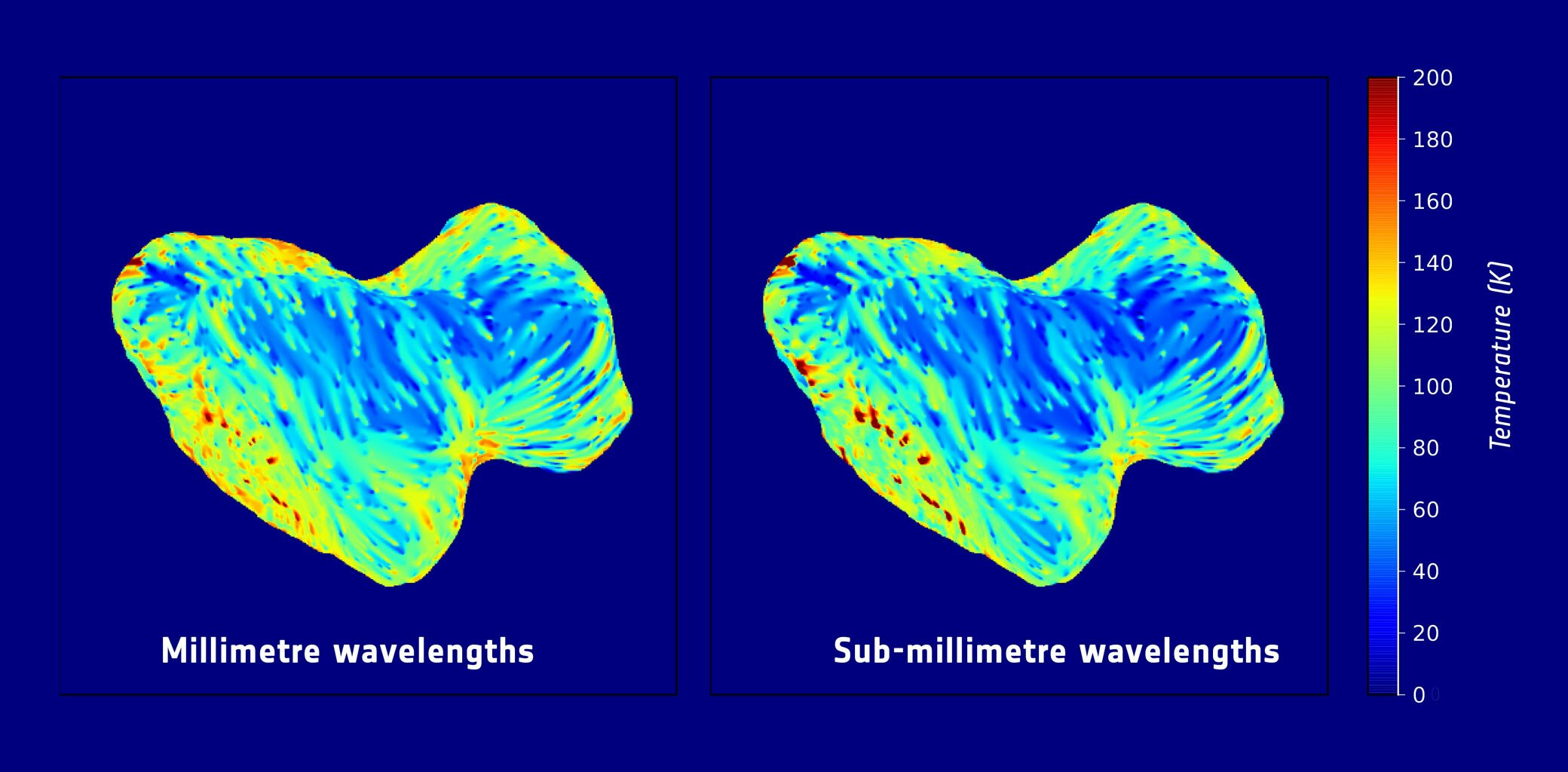
✔Asteroids are made of rock, metals and other elements. Some even contain water💧, astronomers say. Asteroids that are mostly stone sometimes are more like loose piles of rubble. Asteroids that are mostly iron are more, well, rock-solid.
Asteroids contain traces of amino acids and other organic compounds, and some speculate that asteroid impacts may have seeded🌾 the early Earth🌍 with the chemicals necessary to initiate life🌱, or may have even brought life🐛 itself to Earth🌎.
Most asteroids (75%) are made of carbon-based rock. The rest are made of the metals iron and nickel. About half of these are pure iron and nickel; the rest are mixed with silica compounds. Each of the larger metal asteroids contains more iron than has been mined in the entire history of human kind.
Scientists🕵 are very interested in what asteroids are made of because it can help them learn how the solar system was formed🤔. Several spacecraft have visited asteroids to learn more about them.

The physical composition of asteroids is varied and in most cases poorly understood.
Ceres appears to be composed of a rocky core covered by an icy mantle, where Vesta is thought to have a nickel-iron core, olivine mantle, and basaltic crust. 10 Hygiea, however, which appears to have a uniformly primitive composition of carbonaceous chondrite, is thought to be the largest undifferentiated asteroid.
Most of the smaller asteroids are thought to be piles of rubble held together loosely by gravity, though the largest are probably solid. Some asteroids have moons or are co-orbiting binaries: Rubble piles, moons, binaries, and scattered asteroid families are thought to be the results of collisions that disrupted a parent asteroid, or, possibly, a planet.
How big are the Asteroids?🤔❔

✔The largest asteroid is Ceres, which is 1032 kilometers across. The next largest, which is called Pallas, is 588 kilometers across.
Asteroids less than a kilometer across have also been seen. Unofficially the limit has been set at 50 meters, and anything smaller than that is going to be simply called a Meteoroid. With advances in telescopes and particularly for objects that travel close to the Earth🌎, some objects have been seen that are indeed smaller than 50 meters that merely pass nearby the Earth🌠🌍.
Most asteroids are found in the asteroid belt, but not all. Some asteroids orbit closer to the Sun. Asteroids that closely approach Earth are called Near-Earth Asteroids. Sometimes they strike the Earth, burning in the atmosphere as a
meteor. If they are large enough, they might actually hit the surface and become meteorites🌠✨.
What is a ‘Close Approach’? 🤔❔
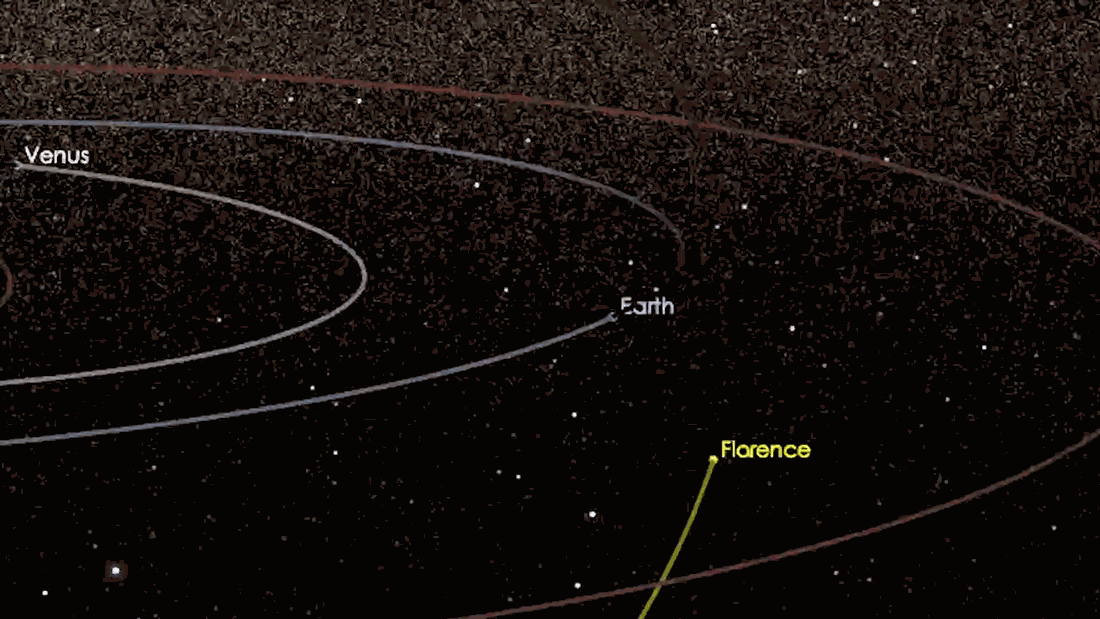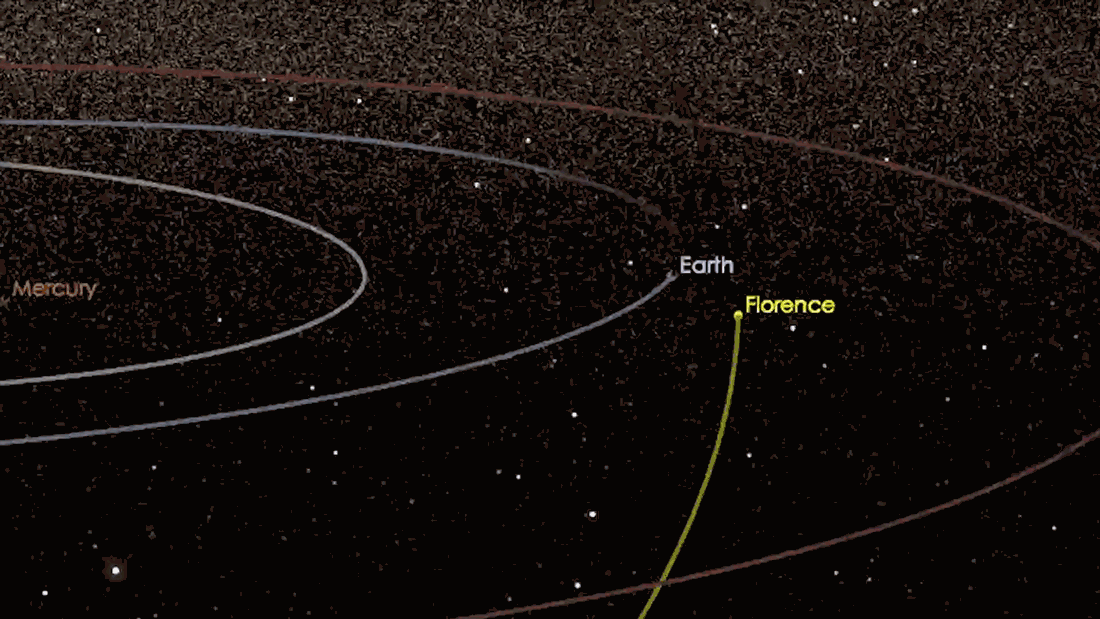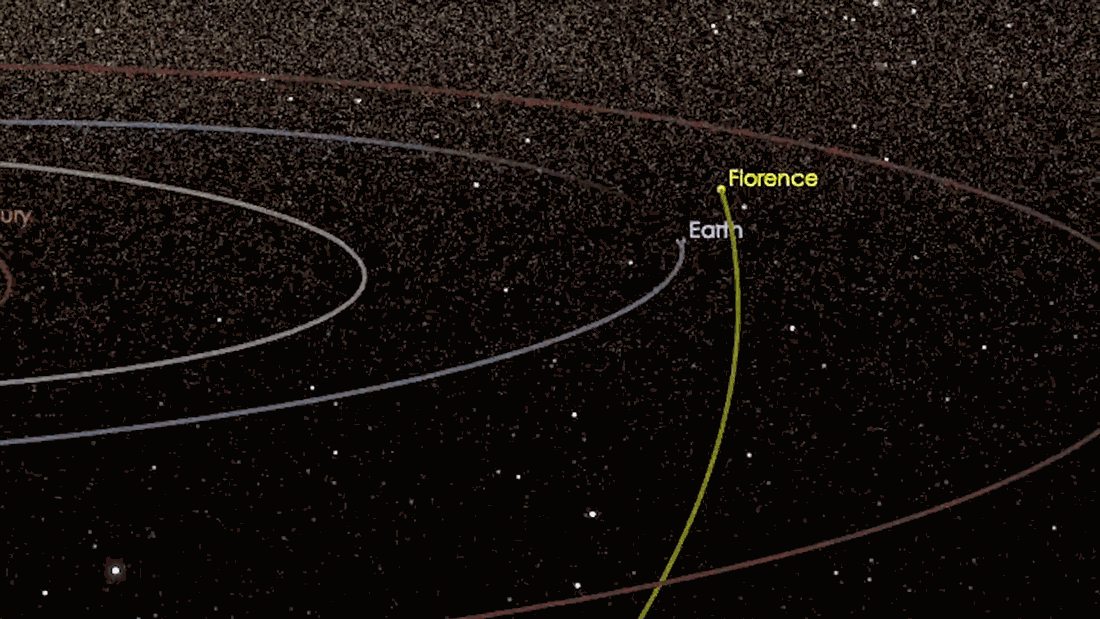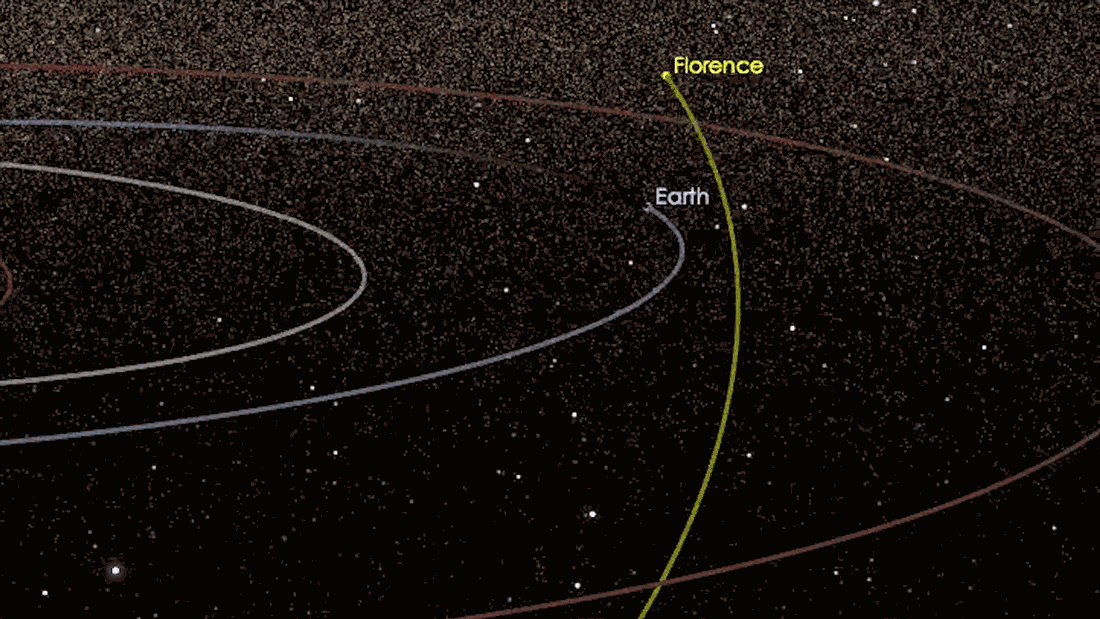
Asteroid close approach: ‘Close’ is very far in astronomical terms.
A Near-Earth Object (NEO) is a any small Solar System body whose orbit bring it to proximity with Earth. As they orbit the Sun🌞, Near-Earth Objects occasionally make a ‘close approach’ to Earth🌎.
Every month dozens of near-earth asteroids come within 0.05au of Earth- that’s about 4,647,790 miles.
So NEOs are not necessarily currently near the Earth, but they can potentially approach the Earth relatively closely– therefore, a ‘close approach’.
Are there asteroids outside of the asteroid belt?🤔❔
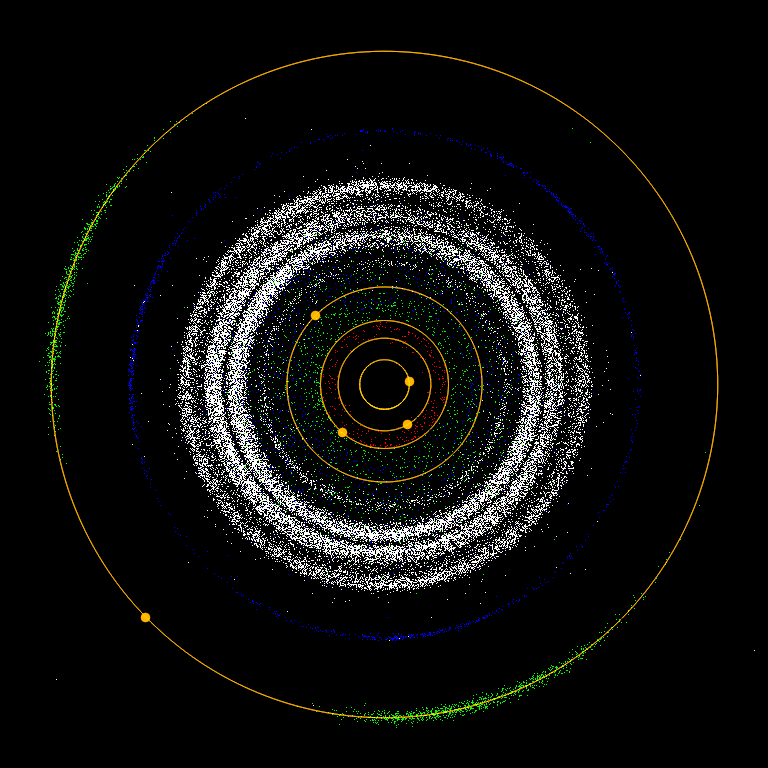
Showing Kirkwood gaps, by showing positions based on their semi-major axis. White colour shows asteroid belt, NASA
✔There are also some asteroids in the outer solar system that are called
Centaurs, although it is hard to determine whether a particular Centaurs is an asteroid, comet, or Kuiper Belt object. For example, the first Centaur to be discovered was Chiron. But some scientists think it is a comet, not an asteroid.
Officially it is both the asteroid 2060 Chiron and the comet 95P/Chiron!
Some asteroids are also found at the stable points 60° behind and ahead of the
orbits of Jupiter and other planets. The points are called Lagrange points and the asteroids found there are called Trojans. Many of the small moons of some planets may have once been asteroids that were captured by the planet’s gravity when they came too close.
Where does asteroid come from?🤔❔
✔Asteroids are leftovers from the formation of our solar system about 4.6 billion years ago. Early on, the birth of Jupiter prevented any planetary bodies from forming in the gap between Mars and Jupiter, causing the small objects that were there to collide with each other and fragment into the asteroids seen today.
What is a rotation period of Asteroids? 🤔❔

About Rotation Period:💫
Very few asteroids with a diameter larger than 100 meters have a rotation period smaller than 2.2 hours. For asteroids rotating faster than approximately this rate, the inertial force at the surface is greater than the gravitational force, so any loose surface material would be flung out. However, a solid object should be able to rotate much more rapidly.
This suggests that most asteroids with a diameter over 100 meters are rubble piles formed through accumulation of debris after collisions between asteroids.
Classification of Asteroids: 🤔❔
✔Asteroids are commonly categorized according to two criteria:
🍥The characteristics of their orbits
🌈Features of their reflectance spectrum
Orbital classification💫
✔Many asteroids have been placed in groups and families based on their orbital characteristics.
Groups are relatively loose dynamical associations, whereas families are tighter and result from the catastrophic break-up of a large parent asteroid sometime in the past.
Families are more common and easier to identify within the main asteroid belt, but several small families have been reported among the Jupiter trojans. Main belt families were first recognized by Kiyotsugu Hirayama in 1918 and are often called Hirayama families in his honor.
About 30–35% of the bodies in the asteroid belt belong to dynamical families. A family has also been associated with the plutoid dwarf planet Haumea.
Quasi-satellites and horseshoe objects
✔Sometimes these horseshoe objects temporarily become quasi-satellite for a few decades or a few hundred years, before returning to their earlier status. Both Earth and Venus are known to have quasi-satellites.
Some asteroids have unusual horseshoe orbit that are co-orbital with Earth or some other planet. Examples are 3753 Cruiten and 2002 AA29.
Such objects, if associated with Earth or Venus or even hypothetically Mercury, are a special class of Aten asteroid. However, such objects could be associated with outer planets as well.
Spectrum Classification
✔The original classification system had three categories: C-type, S-type, and U-type.
C-types for dark carbonaceous objects (75% of known asteroids).
S-types for stony (silicaceous) objects (17% of known asteroids).
U-types for those that did not fit into either C or S.
The two most widely used taxonomies now used are the Tholen classification, an eight-color asteroid survey with 14 asteroid categories and SMASS classification, Small Main-Belt Asteroid Spectroscopic Survey with 24 different types.
Both systems have three broad categories of C, S, and X asteroids, where X consists of mostly metallic asteroids, such as the M-types. There are also several smaller classes.
Problem: there are no assurances that asteroids within the same taxonomic class are composed of similar materials.🙄
What are they named after?🤔❔
The first asteroids were named after mythical heroes and gods much like the major planets. The first to be discovered was named Ceres after the Roman goddess of growing plants (particularly grain) and of motherly love. The second asteroid discovered was called Pallas named after one of the Greek gods of wisdom. Asteroids are also given a number in the order of their discovery, so Ceres is 1, Pallas is 2, and so forth. As the number of know asteroids increased
the supply of mythical names was exhausted so a names from other sources were used.
Some asteroids were named after countries. For example asteroid number 136 is named Austria. Others were named after plants, for example 978 Petunia.
1620 Geographos was named after the National Geographic Society, in
recognition to their efforts at sharing knowledge about the Solar System. Many are named after people both alive and dead. In a couple of cases, like 2309 Mr. Spock, asteroids were named after the discover’s pet cat. This naming has been discouraged, but it still happens occasionally. Even fictional characters have
been used.

Today, names for asteroids can be suggested by the people who discover them.
The names become official after a group of people reviews them to make sure they are not offensive or too much like another name. Due to some automated asteroid scanning observatories and a systematic exploration of the Solar System for near Earth asteroids, almost all new asteroid discoveries are not even getting a name at all, but rather a numerical designation, and it is not
anticipated that they will ever be given a formal name, at least in this century.
How many are there?🤔❔
As of March 2020, the Minor Planets Center had data on 930,000 minor planets in the inner and outer Solar System, of which about 545,000 had enough information to be given numbered designations.
Asteroids that actually cross Earth’s orbital path are known as Earth-crossers. As of June 2016, 14,464 near-Earth asteroids are known and the number over one kilometer in diameter is estimated to be 900–1,000.
Traveling through the asteroid belt in a space ship would not be very much like what you see in a science fiction film.
When was the last time an asteroid hit Earth?🤔❔

66 million years ago. The last known impact of an object of 10 km (6 mi) or more in diameter was at the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago. The energy released by an impactor depends on diameter, density, velocity, and angle.
How big is the asteroid that passed in 2020?🤔❔
An asteroid(2020LD) the size of FIVE blue whales🐳 – the largest animal on Earth🌍 – swung by Earth recently, but astronomers were none the wiser. The space rock has been dubbed 2020 LD and measured in at a whopping 400 feet (122 meters). The asteroid came relatively close to Earth, at just 80% of the distance between Earth and the Moon (190,559 miles) and travelling at a staggering 60,826 miles per hour.
Asteroid 2020 LD passed within the moon’s distance on June 5, but wasn’t discovered until June 7. It’s the 45th known and the largest asteroid to sweep within a lunar-distance of Earth so far in 2020.
✔Radar images show that 2020 BX12 was discovered on 27 January 2020, at least 165 m (541 ft) in diameter, implying a geometric albedo or reflectivity of 0.30 given its absolute magnitude of 20.6. 2020 BX12 appears to have a nearly spheroidal shape, which is commonly observed in other near-Earth objects such as 2005 YU55 and 101955 Bennu.
Which asteroid will hit Earth?🤔❔
✔Apophis2029/2036/2068 approaches. On April 13, 2029, Apophis will pass Earth closer than geosynchronous communication satellites, but will come no closer than 31,200 kilometres (19,400 mi) above Earth’s surface.
What happens if asteroid hit Earth?🤔❔
The more energy is released, the more damage is likely to occur on the ground due to the environmental effects triggered by the impact. Such effects can be shock waves, heat radiation, the formation of craters with associated earthquakes, and tsunamis if water bodies are hit.
Can we live on asteroids?🤔❔
On Earth, we are protected by a magnetic field and our atmosphere, but asteroids lack this defense. One possibility for defense against this radiation is living inside of an asteroid. It is estimated that humans would be sufficiently protected from radiation by burrowing 100 meters deep inside of an asteroid.
How would NASA stop an asteroid?🤔❔
An object with a high mass close to the Earth could be sent out into a collision course with the asteroid, knocking it off course. When the asteroid is still far from the Earth, a means of deflecting the asteroid is to directly alter its momentum by colliding a spacecraft with the asteroid.
What if an asteroid hits the ocean🌊?🤔❔
Depending on their mass and speed, they could hit us hard. But depending on where an asteroid hits, the fallout will vary greatly. … But if an asteroid hits one of our oceans🌊 — water💦 makes up for 70% of our planet’s surface and is therefore a more likely scenario — the scope of the impact is poorly understood.
How much is an asteroid worth?🤔❔
The 16 Psyche asteroid has so much precious heavy metals, it’s estimated to be worth $10,000 quadrillion🤑. A 140-mile wide, potato-shaped asteroid is so rich with precious heavy metals, it’s estimated to be worth $10,000 quadrillion💸.
Does the asteroid belt protect Earth?🤔❔
Astronomers think that if it were not for the giant planet Jupiter exerting its gravitational force on the asteroids in the belt, the inner planets would be constantly bombarded by large asteroids. The presence of Jupiter actually protects Mercury, Venus, Earth🌎, and Mars from repeated asteroid collisions!🌋
Can you walk on an asteroid?🤔❔
HUMANS CAN‘T WALK OR DRIVE ON AN ASTEROID.In reality, even the biggest asteroids have practically no gravity. So anything in contact with the surface could easily drift away. “You don’t land on an asteroid,” said former Apollo astronaut Rusty Schweickart, a longtime advocate of asteroid studies.
Why are asteroids so valuable?🤔❔
In response, it has been suggested that platinum, cobalt and other valuable elements from asteroids may be mined and sent to Earth for profit, used to build solar-power satellites and space habitats, and water processed from ice to refuel orbiting propellant depots
What happens if an asteroid hits the sun🌞?

If an asteroid were to strike land🌋 or a shallow body of water🌊, it would eject an enormous amount of dust🌪, ash, and other material into the atmosphere, blocking the radiation from the Sun🌥. This would cause the global temperature to decrease drastically🌇.
Does Space agency have a plan for an asteroid?🤔❔
In June 2018, the US National Science and Technology Council warned that America is unprepared for an asteroid impact event, and developed and released the “National Near-Earth Object Preparedness Strategy Action Plan” to better prepare.
Is There Gold👑 on asteroids?🤔❔
S-type asteroids carry little water💦 but look more attractive because they contain numerous metals including: nickel, cobalt and more valuable metals such as gold👑, platinum and rhodium🤑.
Can you jump off an asteroid?🤔❔
We have not enough information about the densities of asteroids, about all we can say is that the object can be up to 4 km across if it’s as dense as our planet, or perhaps 9 km if it’s a “rubble pile.” So a human could easily hop the 1.5-km span from 5381 Sekhmet to its moon and back, since both bodies are 1 km or less in size.
How can we stop asteroids?🤔❔
If the object is very large but is still a loosely-held-together rubble pile, a solution is to detonate one or a series of nuclear explosive devices alongside the asteroid, at a 20-meter (66 ft) or greater stand-off height above its surface, so as not to fracture the potentially loosely-held-together object.
Can I buy an asteroid?🤔❔
Legally, nobody can own an asteroid, but the US Space Act of 2015 allows companies to own the materials they mine from bodies in space.
What would happen if a 5 km asteroid hit Earth?🤔❔
If an asteroid or comet with the diameter of about 5 km (3.1 mi) or more were to hit in a large deep body of water or explode before hitting the surface, there would still be an enormous amount of debris ejected into the atmosphere🌫.
Why do asteroids burn up?🤔❔
When a meteoroid (small asteroid) enters the atmosphere, it compresses the air in front of it. That compression heats the air, which in turn heats the object, causing it to glow and vaporize.
What size asteroid is dangerous?🤔❔
Asteroids larger than approximately 35 meters across can pose a threat to a town or city. However the diameter of most small asteroids is not well determined, as it is usually only estimated based on their brightness and distance, rather than directly measured, e.g. from radar observations.
✔🌑Four largest Asteroid:

❓Ceres is the only asteroid with a fully ellipsoidal shape and hence the only one that is a dwarf planet. It has a much higher absolute magnitude than the other asteroids, of around 3.32, and may possess a surface layer of ice. Like the planets, Ceres is differentiated: it has a crust, a mantle and a core. No meteorites from Ceres have been found on Earth.

➰Vesta, too, has a differentiated interior, though it formed inside the Solar System’s frost line, and so is devoid of water. Aside from the large crater at its southern pole, Rheasilvia, Vesta also has an ellipsoidal shape. Vesta is the parent body of the Vestian family and other V-type asteroids, and is the source of the HED meteorites, which constitute 5% of all meteorites on Earth.
🔶Pallas is unusual in that, like Uranus, it rotates on its side, with its axis of rotation tilted at high angles to its orbital plane. Its composition is similar to that of Ceres: high in carbon and silicon, and perhaps partially differentiated. Pallas is the parent body of the Palladian family of asteroids.
🐍Hygiea is the largest carbonaceous asteroid and, unlike the other largest asteroids, lies relatively close to the plane of the elliptic. It is the largest member and presumed parent body of the Hygiean family of asteroids. Because there is no sufficiently large crater on the surface to be the source of that family, as there is on Vesta, it is thought that Hygiea may have been completely disrupted in the collision that formed the Hygiean family, and recoalesced after losing a bit less than 2% of its mass. Hygiea has a nearly spherical shape, which is at consistent both with it being in hydrostatic equilibrium (dwarf planet).
Exploration:🔭🚀🛰
Until the age of space travel, objects in the asteroid belt were merely pinpricks of light in even the largest telescopes and their shapes and terrain remained a mystery. The best modern ground-based telescopes and the Earth-orbiting Hubble Space Telescope can resolve a small amount of detail on the surfaces of the largest asteroids, but even these mostly remain little more than fuzzy blobs.
Limited information about the shapes and compositions of asteroids can be inferred from their light curves (their variation in brightness as they rotate) and their spectral properties, and asteroid sizes can be estimated by timing the lengths of star occulations (when an asteroid passes directly in front of a star).
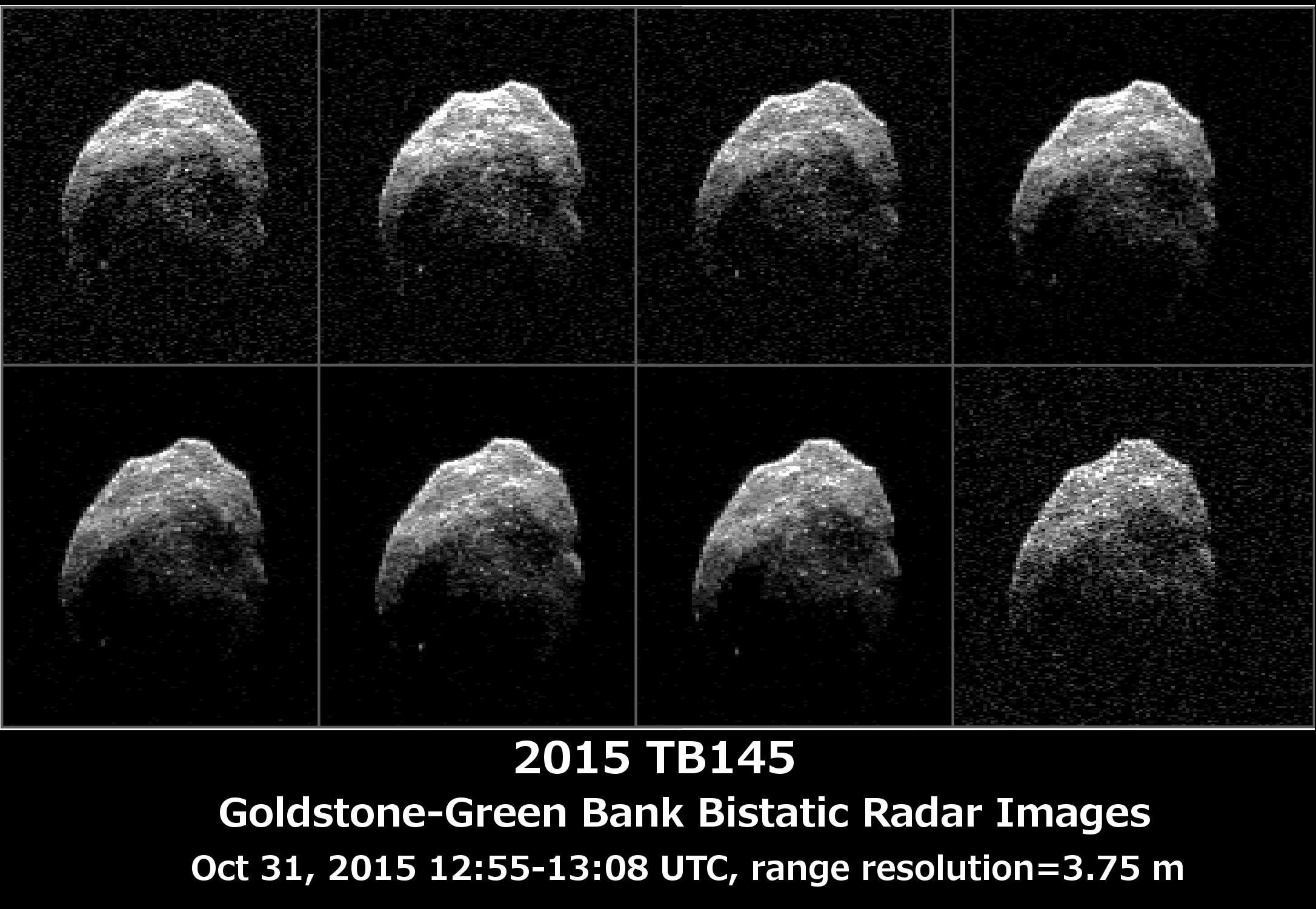

Radar imaging can yield good information about asteroid shapes and orbital and rotational parameters, especially for near-Earth asteroids. In terms of delta-V and propellant requirements, NEOs are more easily accessible than the Moon.
In September 2016, NASA launched the OSIRIS-REx sample return mission to asteroid 101955Bennu, which it reached in December 2018. As of June 2019, the probe is in orbit around the asteroid.
Planned and Future Missions:🛰🕵🚀🌑🌍🔭🌠
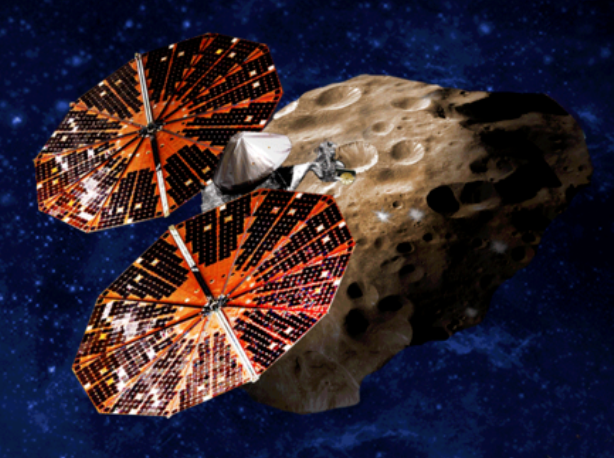

On 19 June 2014, NASA reported that asteroid 2011 MD was a prime candidate for capture by a robotic mission, perhaps in the early 2020s.
It has been suggested that asteroids might be used as a source of materials that may be rare or exhausted on Earth🌍 (asteroid mining), or materials for constructing space habitates. Materials that are heavy and expensive to launch from Earth may someday be mined from asteroids and used for space manufacturing and construction.
In the U.S. Discovery program the Psyche spacecraft proposal to 16 Psyche and Lucy spacecraft to Jupiter trojans made it to the semi-finalist stage of mission selection.
In January 2017, Lucy and Psyche mission were both selected as NASA’s Discovery program missions 13 and 14 respectively.
Last Fact About Asteroid and Dinosaurs:🌎🌠💥🌋🦄

Did the asteroid killed the dinosaur?🤔❔
There is strong evidence that the mass extinction that killed the dinosaurs 65 million years ago was caused by an asteroid at least 12km wide in Mexico. If that had not happened, would humans be walking the Earth today?
The Chicxulub crater (Mayan) is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Its center is located near the town of Chicxulub, after which the crater is named.
Content Writer: Chanchal Pal, @Technoभौतिकी India